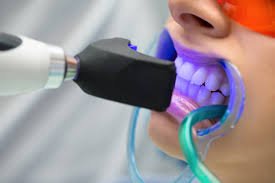
Teeth whitening is a popular cosmetic procedure that aims to improve the appearance of your smile by removing stains and discoloration from your teeth. While the process might seem simple, there’s a fascinating science behind how teeth whitening works. Understanding the mechanisms behind this treatment can help you make informed decisions about whitening options and expectations. In this article, we’ll explore the science of teeth whitening and how it effectively brightens your smile.
Understanding Tooth Discoloration
Before diving into how whitening works, it’s important to understand why teeth become discolored in the first place. Tooth discoloration occurs in two main ways: extrinsic and intrinsic staining.
- Extrinsic Staining: This type of discoloration occurs on the surface of the teeth and is caused by external factors like food, beverages (coffee, tea, red wine), smoking, or poor oral hygiene. These stains can often be removed through professional cleaning or whitening treatments.
- Intrinsic Staining: This type of discoloration occurs deeper inside the tooth and is often caused by aging, certain medications, or trauma to the tooth. Intrinsic stains are more difficult to treat but can be lightened through certain whitening techniques.
How Teeth Whitening Works: The Chemistry Behind It
Teeth whitening treatments, whether over-the-counter or professional, typically involve the use of bleaching agents such as hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide. These chemicals work by breaking down the molecules that cause stains on the tooth enamel.
- Hydrogen Peroxide: Hydrogen peroxide is the most commonly used bleaching agent in teeth whitening treatments. It penetrates the enamel (the outer layer of the tooth) and breaks down into water and oxygen molecules. The oxygen molecules then interact with the stain molecules, breaking them apart and effectively lifting the discoloration.
- Carbamide Peroxide: Carbamide peroxide is another common ingredient in teeth whitening products. It breaks down into hydrogen peroxide and urea. The hydrogen peroxide, as mentioned above, then works to break apart the stain molecules.
The breakdown of these stain molecules allows the teeth to appear whiter and brighter. The effectiveness of whitening treatments largely depends on the strength of the peroxide concentration and the duration of exposure to the bleaching agent.
The Role of Enamel in Teeth Whitening
To understand how whitening works, it’s important to know a little about the tooth structure. The outer layer of the tooth, called enamel, is what gives teeth their white appearance. Enamel is semi-translucent, and beneath it lies the dentin, a yellowish tissue that contributes to the natural color of the tooth. Over time, enamel can become worn down or stained, exposing the dentin and causing teeth to appear yellow.
Teeth whitening works by either lightening the stains on the enamel or, in the case of intrinsic stains, by changing the color of the dentin itself. However, it’s important to note that enamel is a delicate substance, and overuse of whitening products can cause it to wear down, leading to increased sensitivity or even damage.
Types of Teeth Whitening Treatments
There are several methods for whitening teeth, each utilizing different strengths of peroxide to achieve the desired results. Here are some common whitening options:
- In-Office Professional Whitening: This method is done under the supervision of a dentist. It typically involves a high concentration of hydrogen peroxide, which can produce immediate results. Dentists may use light or heat to enhance the whitening effect, but the treatment generally takes about an hour to complete.
- At-Home Whitening Kits: These products include whitening gels, strips, or trays that contain a lower concentration of hydrogen peroxide. While the results take longer to achieve, at-home treatments can be effective when used consistently. These kits may take a few days or weeks to show noticeable results.
- Whitening Toothpastes: Whitening toothpastes contain mild abrasives and chemicals that help remove surface stains. While they can help maintain a bright smile, they are not as effective as bleaching treatments for deeper discoloration.
Conclusion
Teeth whitening is a popular and effective way to brighten your smile, thanks to the chemistry of peroxide-based bleaching agents. Whether you choose a professional treatment or an at-home kit, whitening can help remove stains and improve the appearance of your teeth. However, it’s essential to use these products correctly and maintain good oral hygiene to keep your teeth looking their best. Understanding the science behind teeth whitening can help you make informed decisions and achieve a healthier, more radiant smile.